Cambodia, a country steeped in history and rich cultural heritage, is a land of mesmerizing traditions, vibrant festivals, and profound spirituality. From the awe-inspiring temples of Angkor Wat to the gentle smiles of its people, Cambodian culture is a tapestry of ancient customs and modern influences. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the essence of Cambodian culture and traditions, offering insights into what makes this Southeast Asian nation truly unique.
The Heart of Cambodian Culture: Spirituality and Religion
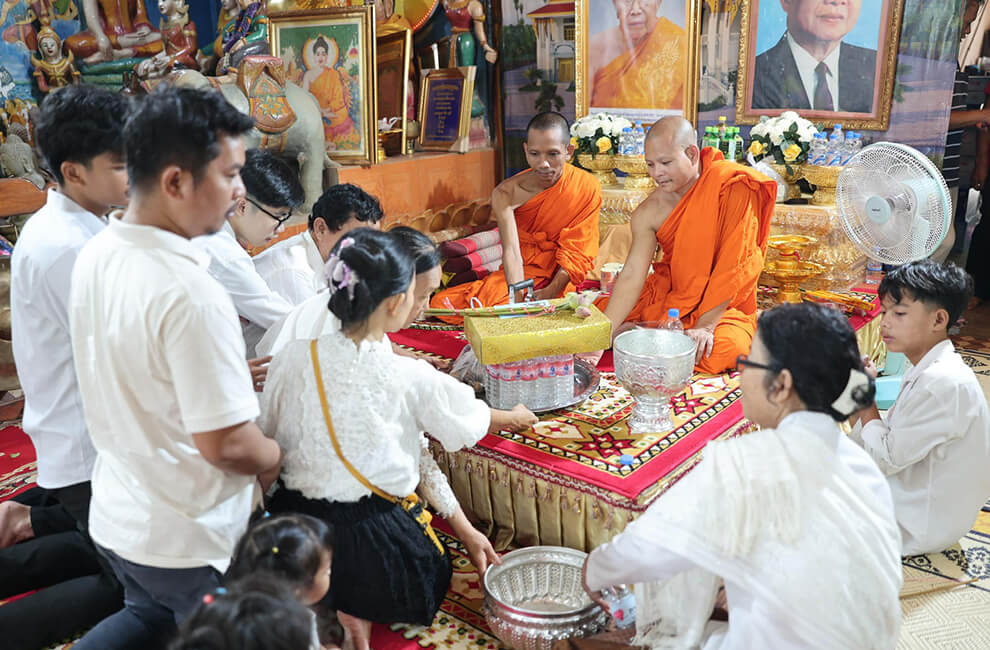
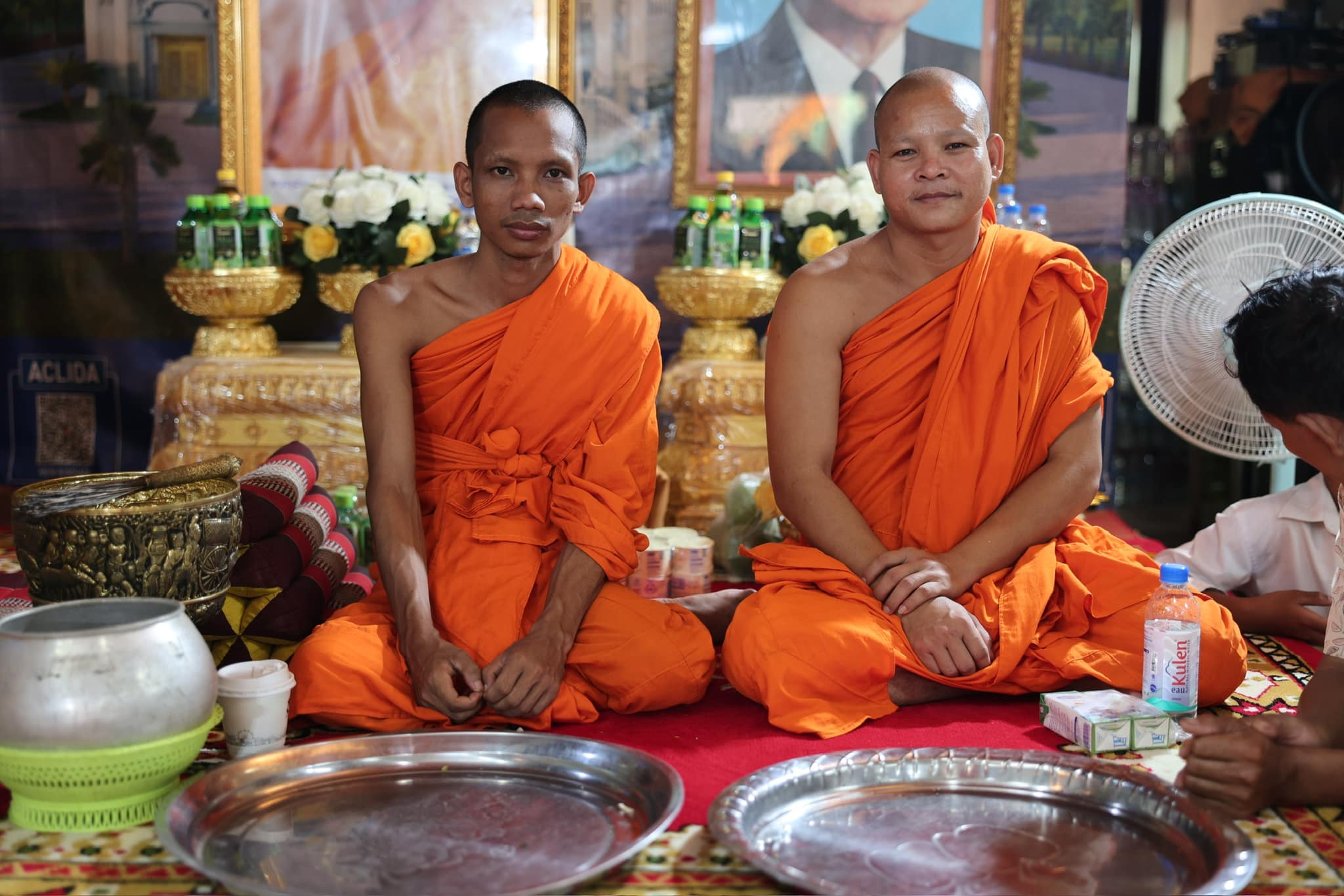
At the core of Cambodian culture lies Theravada Buddhism, which shapes the daily lives, values, and traditions of the Khmer people. Over 95% of Cambodians practice Buddhism, and its influence is evident in everything from architecture to social norms.
- Monks and Monasteries: Monks are highly respected in Cambodian society. Monasteries, or wats, serve as centers of learning, meditation, and community gatherings.
- Daily Rituals: Many Cambodians start their day by offering food to monks, a practice known as dak bat. This act of giving is believed to bring merit and good karma.
- Spiritual Festivals: Religious festivals like Pchum Ben (Ancestors’ Day) and Visak Bochea (Buddha’s Birthday) are deeply rooted in Buddhist traditions and are celebrated with great devotion.

The Legacy of the Khmer Empire
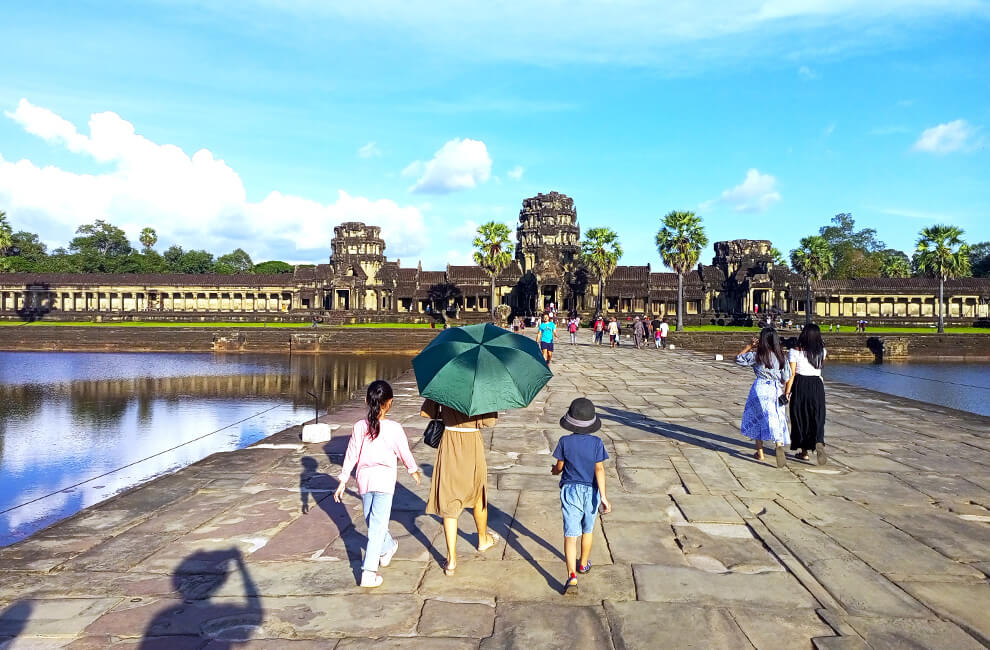
The Khmer Empire, which ruled much of Southeast Asia from the 9th to the 15th century, left an indelible mark on Cambodian culture. The empire’s architectural marvels, such as Angkor Wat, symbolize the ingenuity and artistic prowess of the Khmer people.
- Angkor Wat: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, Angkor Wat is not only a symbol of Cambodia but also a testament to the empire’s devotion to Hinduism and later Buddhism.
- Traditional Dance: The classical Apsara dance, inspired by the carvings of Angkor Wat, is a graceful art form that tells stories of ancient myths and legends.
- Khmer Language and Script: The Khmer language, with its unique script, is one of the oldest in Southeast Asia and remains a cornerstone of national identity.
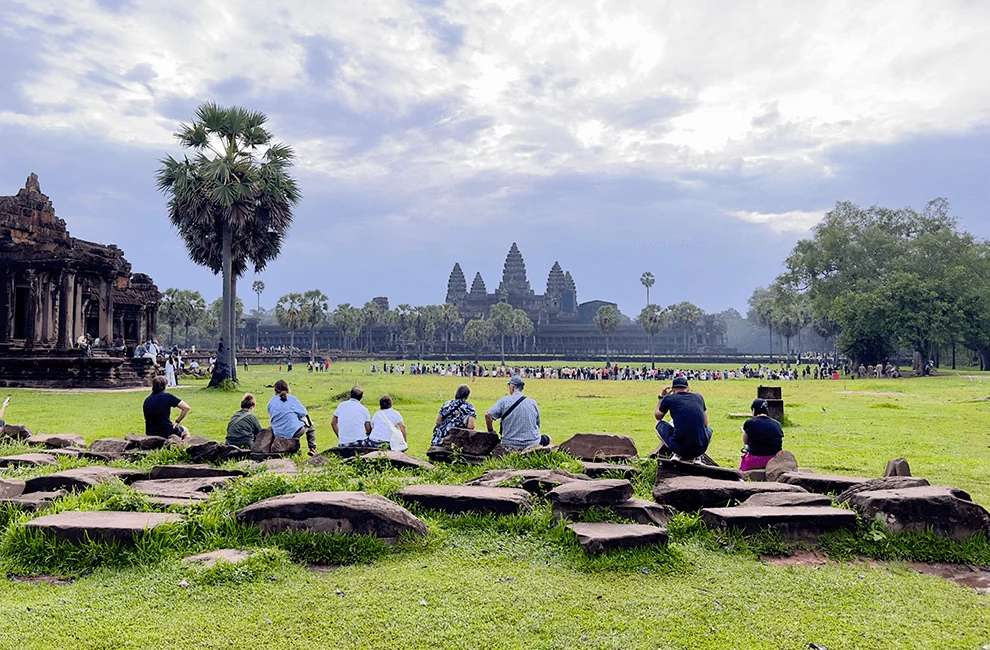

Family is the cornerstone of Cambodian society. The concept of collectivism is deeply ingrained, with an emphasis on harmony, respect, and mutual support.
- Hierarchy and Respect: Cambodian culture places great importance on age and social status. Younger individuals are expected to show respect to their elders through gestures like the sampeah, a traditional greeting involving a slight bow with palms pressed together.
- Gender Roles: While traditional gender roles are still prevalent, modern Cambodia is seeing a shift toward greater gender equality, especially in urban areas.
- Community Spirit: Villages often function as extended families, with communal activities and shared responsibilities.
$98
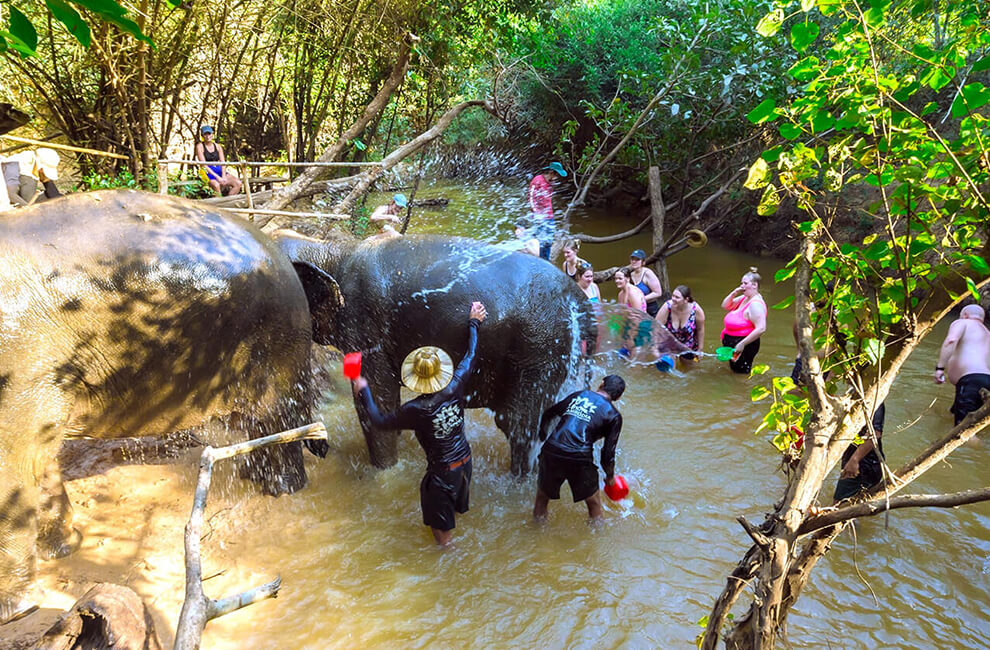

Cambodia Elephant Sanctuary
- Duration: 4 hours
- Destination: Siem Reap
$89
Festivals and Celebrations: A Window into Cambodian Traditions
Cambodia’s calendar is filled with vibrant festivals that reflect its cultural and religious heritage. These celebrations are a time for families to come together, honor their traditions, and express their devotion.
- Khmer New Year (Choul Chnam Thmey): Celebrated in April, this three-day festival marks the end of the harvest season. Families clean their homes, visit temples, and engage in traditional games and dances.
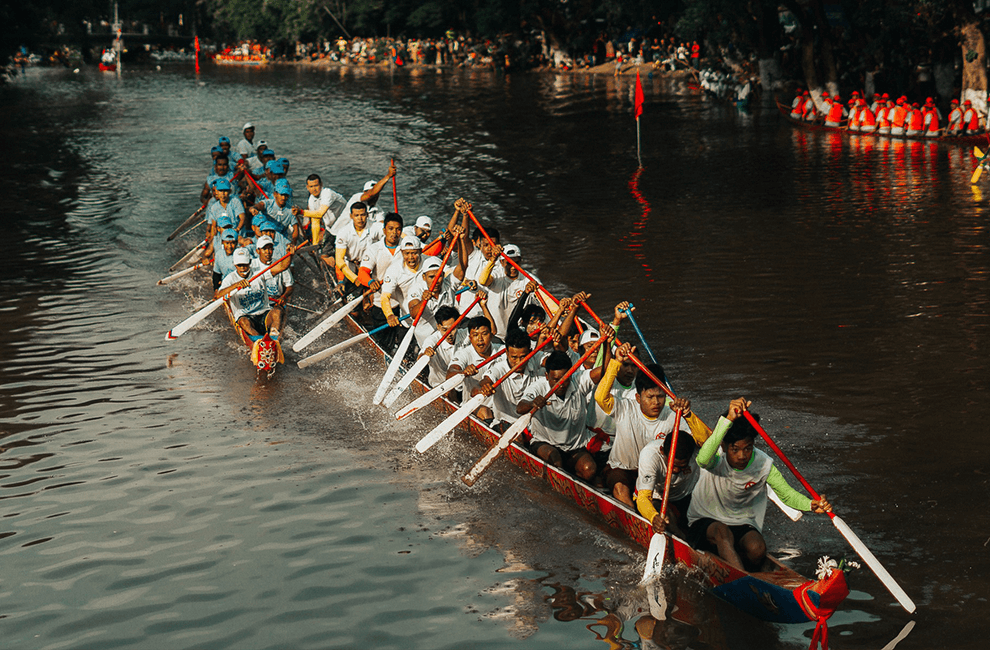
- Water Festival (Bon Om Touk): Held in November, this festival celebrates the reversal of the Tonle Sap River’s flow. It features boat races, fireworks, and illuminated floats.
- Royal Ploughing Ceremony: An ancient agricultural ritual that marks the beginning of the planting season, symbolizing prosperity and good harvests.

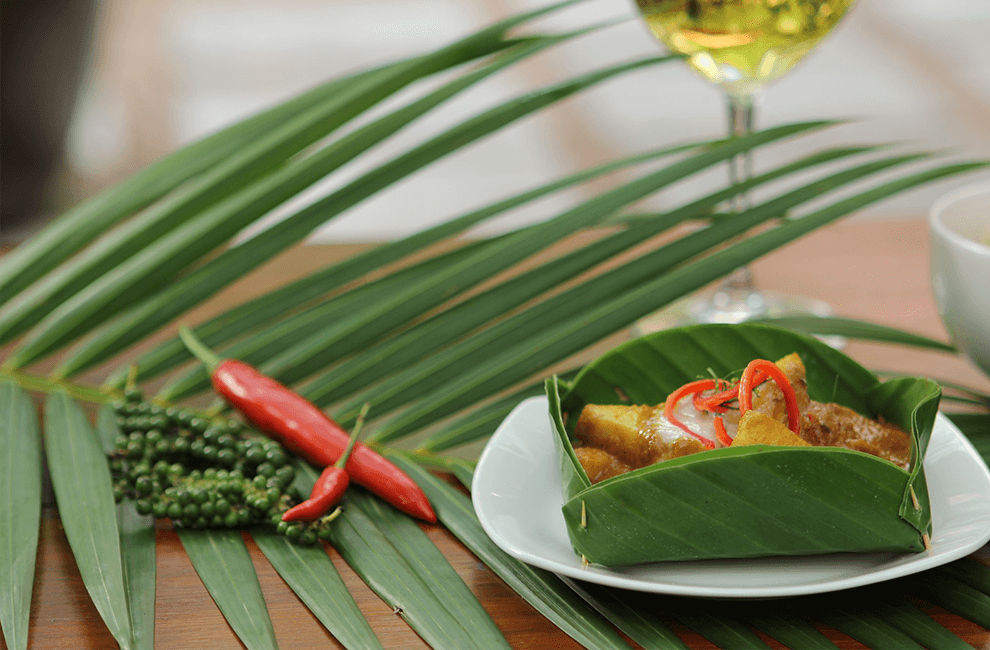
Cambodian Cuisine: A Feast for the Senses
Cambodian cuisine, or Khmer cuisine, is a delightful blend of flavors, textures, and aromas. While it shares similarities with Thai and Vietnamese food, it has its own distinct identity.
- Staple Foods: Rice is the centerpiece of every meal, often accompanied by fresh vegetables, fish, and aromatic herbs.
- Signature Dishes:
- Amok: A creamy curry made with fish, coconut milk, and spices, steamed in banana leaves.
- Bai Sach Chrouk: Grilled pork served with rice and pickled vegetables.
- Nom Banh Chok: A traditional breakfast dish of rice noodles topped with fish-based green curry.
- Street Food Culture: Cambodian street food, such as fried insects and sweet desserts, offers a glimpse into the country’s culinary diversity.

Traditional Arts and Crafts
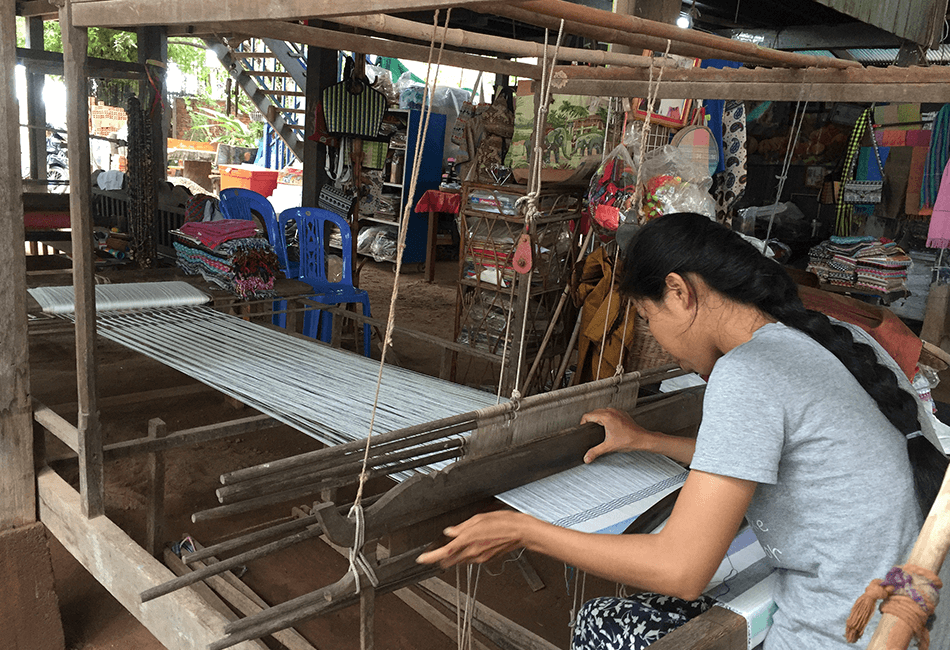
Cambodia’s artistic heritage is a reflection of its cultural depth and creativity. From intricate silk weaving to stone carving, these crafts have been passed down through generations.
- Silk Weaving: Cambodian silk is renowned for its quality and intricate patterns. The art of silk weaving is particularly prominent in rural areas like Takeo and Siem Reap.
- Pottery and Ceramics: The ancient town of Kompong Chhnang is famous for its traditional pottery, which is both functional and decorative.
- Shadow Puppetry: Known as Sbek Thom, this traditional art form uses leather puppets to depict scenes from the Reamker, the Cambodian version of the Ramayana.

Modern Influences and Cultural Preservation
While Cambodia embraces modernity, there is a strong effort to preserve its cultural heritage. Organizations and initiatives are working to revive traditional arts, protect historical sites, and promote Khmer culture globally.
- Education and Awareness: Schools and cultural institutions are incorporating traditional arts and history into their curricula.
- Tourism and Cultural Exchange: Tourism plays a vital role in promoting Cambodian culture, with visitors flocking to experience its temples, festivals, and cuisine.
- Challenges: Despite these efforts, Cambodia faces challenges such as globalization and the loss of traditional knowledge, making cultural preservation more important than ever.

Understanding Cambodian etiquette is essential for visitors and those looking to engage with the culture respectfully.
- Dress Modestly: When visiting temples or rural areas, it is important to dress modestly, covering shoulders and knees.
- Remove Shoes: It is customary to remove shoes before entering homes and sacred spaces.
- Respect for Monks: Women should avoid physical contact with monks and offer items indirectly.
$52
Phnom Penh Secrets Full-Day Tour
- Duration: 8 hours
- Destination: Phnom Penh
$110
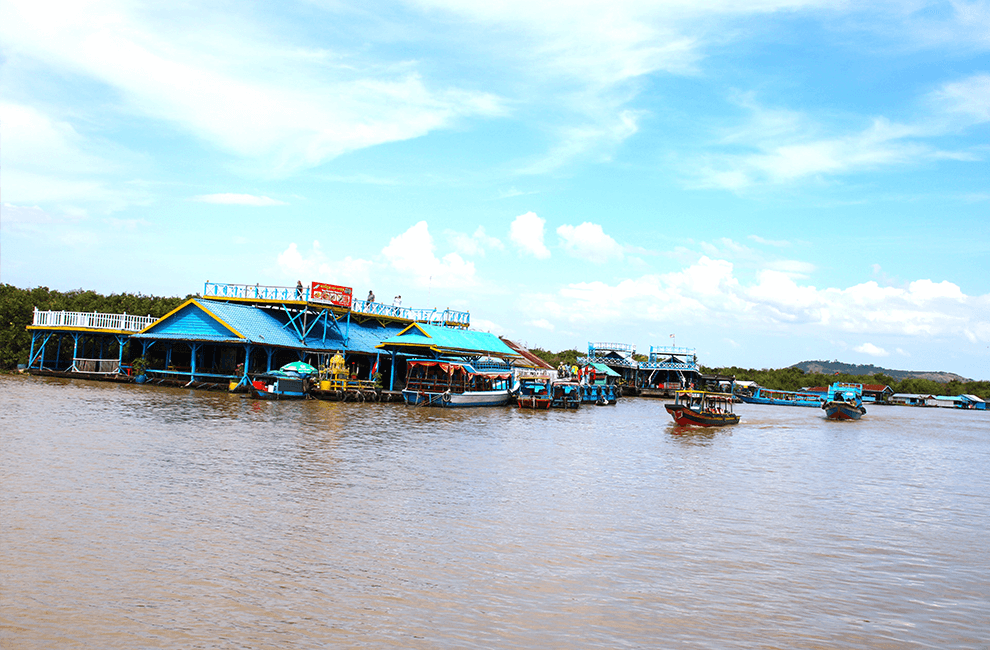
The Role of Nature in Cambodian Culture
Cambodia’s natural beauty is deeply intertwined with its cultural identity. The Mekong River, Tonle Sap Lake, and lush landscapes are not only vital to the country’s economy but also hold spiritual significance.
- Animist Beliefs: Many Cambodians practice animism, believing that spirits inhabit natural elements like trees, rivers, and mountains.
- Eco-Tourism: Efforts are being made to promote sustainable tourism that respects and preserves Cambodia’s natural heritage.

Why Cambodian Culture Matters
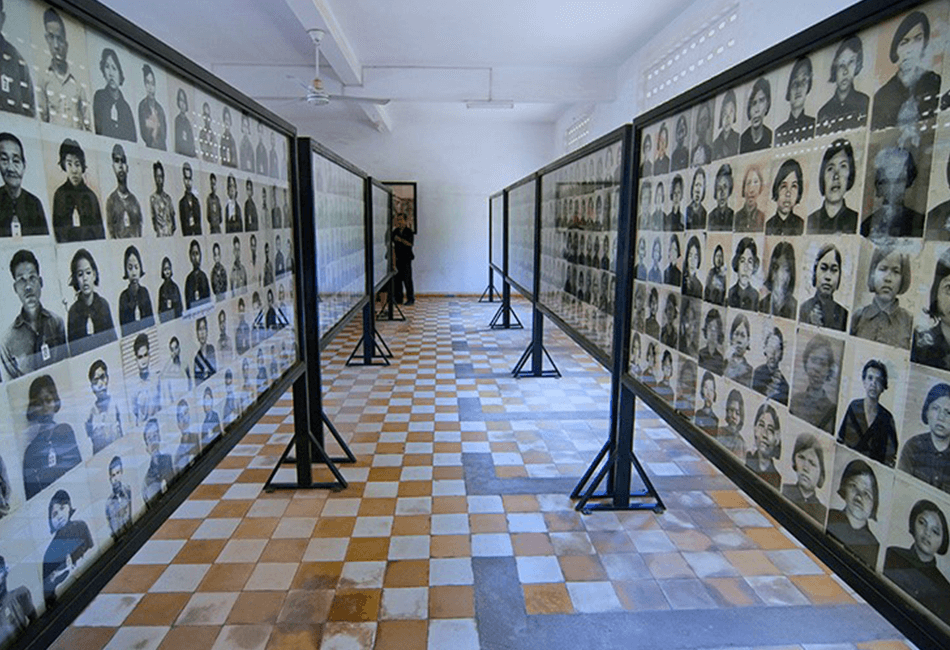
Cambodian culture is a testament to the resilience and creativity of the Khmer people. Despite the challenges of history, including the Khmer Rouge regime, Cambodia has preserved its traditions and continues to celebrate its rich heritage. By understanding and appreciating Cambodian culture, we not only honor its past but also contribute to its future.
Wrapping Up
Cambodian culture and traditions are a vibrant blend of spirituality, history, and community. From the grandeur of Angkor Wat to the simplicity of a family meal, every aspect of Cambodian life tells a story of resilience, faith, and beauty. Whether you’re planning a visit or simply curious about this fascinating culture, exploring Cambodia’s traditions is a journey into the heart of Southeast Asia.







